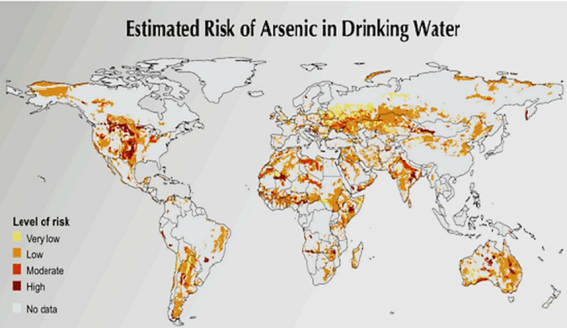
- Arsenic is a naturally occurring element found in the earth’s crust. Erosion, weathering, and industrial runoff can deposit arsenic into our aquifers.
- EPA established a Maximum Contamination Level for Arsenic of 10 micrograms per liter (µg/L) or parts per billion (ppb) in 2001. In amounts over 65mg arsenic is considered to be toxic to the human body and in smaller amounts known to impact cancer growth and diabetes development.
- Fortunately, soluble arsenite(+3) can easily be oxidized to insoluble arsenate(+5). Arsenate as an insoluble precipitate will co-precipitate with iron when introduced to an oxidant, and be physically filtered out.


Learn More
Learn More